JAMB Syllabus for Biology 2026/2027 & Textbooks
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 JAMB Syllabus for Biology 2026/2027
- 3 Part A: Variety of Organisms:
- 4 Part B: Form & Functions:
- 5 9. Co-ordination and Control:
- 6 Part C: Ecology:
- 7 1. Factors affecting the distribution of Organisms:
- 8 2. Symbiotic Interactions of Plants and Animals:
- 9 3. Natural Habitats:
- 10 4. Local (Nigerian Biomes)
- 11 5. The Ecology of Populations:
- 12 6. Soil:
- 13 7. Humans and Environment:
- 14 Part D: Heredity and Variations:
- 15 1. Variation in Population:
- 16 2. Heredity:
- 17 Part E: Evolution:
- 18 1. Theories of Evolution:
- 19 JAMB Biology Syllabus 2026 Recommended Textbook
Introduction
The JAMB Syllabus for Biology 2026/2027 is a comprehensive listing of topics from which questions would be set on all subject areas. The syllabus has been specifically designed to guide candidates to adequately prepare for the examination.
Below is the JAMB 2025 Syllabus for Biology:
JAMB Syllabus for Biology 2026/2027
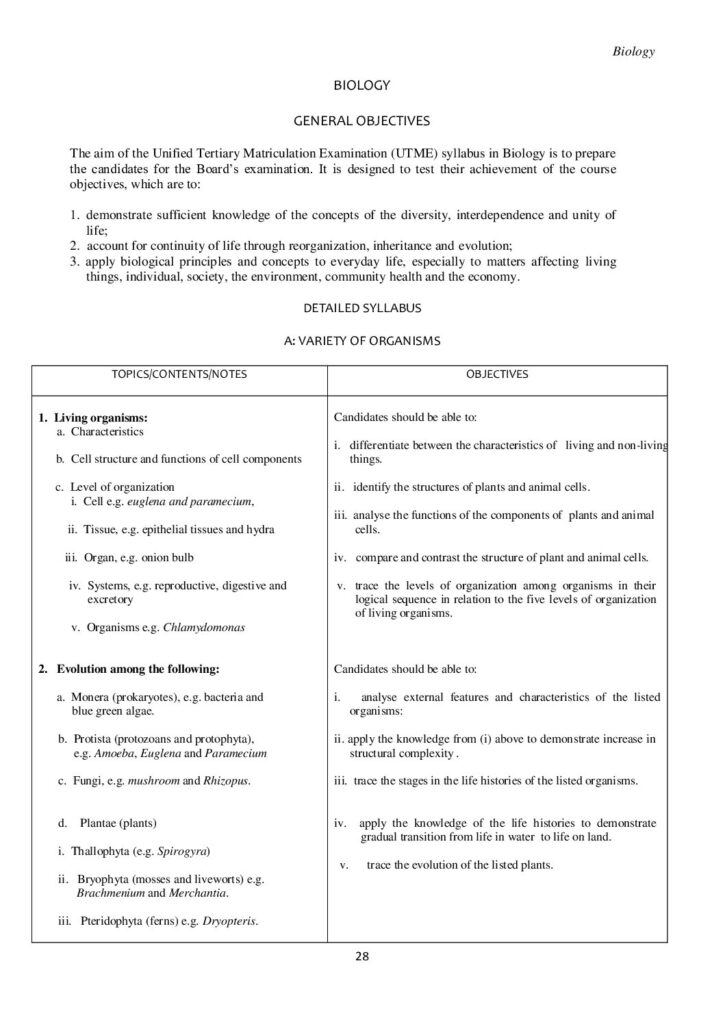
Part A: Variety of Organisms:
1. Living organisms:
(a) Characteristics
(b) Cell structure and functions of cell Components
(c) Level of organization
i. Cell e.g. euglena and paramecium
ii. Tissue, e.g. epithelial tissues and hydra
iii. Organ, e.g. leaf and heart
iv. Systems, e.g. reproductive, digestive and excretory
v. Organisms e.g. Chlamydomonas.
2. Evolution among the following:
(a). Monera (prokaryotes), e.g. bacteria and blue green algae.
(b). Protista (protozoans and protophyta), e.g. Amoeba, Euglena and Paramecium
(c). Fungi, e.g. mushroom and Rhizopus.
(d). Plantae (plants)
i. Thallophyta (e.g. Spirogyra)
ii. Bryophyta (mosses and liveworts) e.g. Bryachymenium and Merchantia.
iii. Pteridophyta (ferns) e.g. Dryopteris.
iv. Spermatophyta (Gymnospermae and Angiospermae)
– Gymnosperms e.g. Cycads and conifers.
– Angiosperms (monocots, e.g. maize; dicots, e.g. water leaf)
(e). Animalia (animals)
- i. Invertebrates
– coelenterate (e.g. Hydra)
– Platyhelminthes (flatworms) e.g. Taenia
– Nematoda (roundworms)
– Annelida (e.g. earthworm)
– Arthropoda (insects) e.g. Millipedes, ticks, mosquito, cockroach, housefly, bee, butterfly
– Mollusca (e.g. snails)
ii. Multicellular animals (vertebrates)
– pisces (cartilaginous and bony fish)
– Amphibia (e.g. toads and frogs)
– Reptilia (e.g. lizards, snakes and turtles)
– Aves (birds)
– Mammalia (mammals)
(a) Structural/functional and behavioural adaptations of Organism
(b). Adaptive colouration and its functions
(c). Behavioural adaptations in social animals
(d). Structural adaptations in organisms.
Part B: Form & Functions:
1. Internal Structure of a Flowering Plant:
(a)
i. Root
ii. Stem
iii. Leaf
(b). Internal structure of a mammal
2. Nutrition:
(a). Modes of nutrition:
i. Autotrophic
ii. Heterotrophic
(b) Types of Nutrition
(c) Plant nutrition:
i. Photosynthesis
ii. Mineral requirements (macro and micro-nutrients)
(d) Animal Nutrition:
i. Classes of food substances; carbohydrates, proteins, fats and oils, vitamins, mineral salts and water
ii. Food tests (e.g. starch, reducing sugar, protein, oil, fat etc.
iii. The mammalian tooth (structures, types and functions)
iv. Mammalian alimentary canal
v. Nutrition process (ingestion, digestion, absorption, and assimilation of digested
food.
3. Transport:
(a). Need for transportation
(b). Materials for transportation. Excretory products, gases, manufactured food, digested food, nutrient, water and hormones)
(c). Channels for transportation
i. Mammalian circulatory system (heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries)
ii Plant vascular system (phloem and xylem)
(d) Media and processes of mechanism for transportation.
4. Respiration:
(a). Respiratory organs and surfaces
(b). The mechanism of gaseous exchange in:
i. Plants
ii. Mammals
(c). Aerobic respiration
(d). Anaerobic respiration
5. Excretion:
(a). Types of excretory structures: contractile vacuole, flamecell, nephridium, Malpighian tubule, kidney, stoma and lenticel.
(b). Excretory mechanisms:
i. Kidneys
ii. lungs
ii. skin
(c). Excretory products of plants
6. Support and Movement:
(a). Tropic, tactic, nastic and sleep movements in plants
(b). Supporting tissues in animals
(c). Types and functions of the skeleton
i. Exoskeleton
ii. Endoskeleton
iii. Functions of the skeleton in animals
7. Reproduction:
(a). A sexual reproduction
i. Fission as in Paramecium
ii. Budding as in yeast
iii. Natural vegetative propagation
iv. Artificial vegetative propagation.
(b). sexual reproduction in flowering plants
i. Floral parts and their functions
ii. Pollination and fertilization
iii. products of sexual reproduction
(a). Meaning fo grwoth
(c) Reproduction in mammals
(i) structures and functions of the male and female reproductive organs
(ii) Fertilization and development. (Fusion of gametes)
8. Growth:
(b). Germination of seeds and condition necessary for germination of seeds.
9. Co-ordination and Control:
(a). Nervous coordination:
i. the components, structure and functions of the central nervous system;
ii. The components and functions of the peripheral nervous systems;
iii. Mechanism of transmission of impulses;
iv. Reflex action
(b). The sense organs
i. skin (tactile)
ii. nose (olfactory)
iii. tongue (taste)
iv. eye (sight)
v. ear (auditory)
(c). Hormonal control
i. animal hormonal system
– Pituitary
– thyroid
– parathyroid
– adrenal gland
– pancreas
– gonads
ii. Plant hormones
(phytohormones)
(d) Homeostasis
(i) Body temperature regulation
(ii) Salt and water regulation
Part C: Ecology:
1. Factors affecting the distribution of Organisms:
i. Abiotic
ii. Biotic
2. Symbiotic Interactions of Plants and Animals:
(a) Food chains, food webs and trophic levels
(b) Energy flow in the ecosystem.
(c) Nutrient cycling in nature
i. carbon cycle
ii. water cycle
iii. Nitrogen cycle
3. Natural Habitats:
(a) Aquatic (e.g. ponds, streams, lakes seashores and mangrove swamps)
(b) Terrestrial/arboreal (e.g. tree-tops of oil palm, abandoned farmland or a dry grassy (savanna) field, and burrow or hole.
4. Local (Nigerian Biomes)
(a). Tropical rainforest
(b). Guinea savanna (southern and northern)
(c). Sudan Savanna
(d). Desert
(e). Highlands of montane forests and grasslands of the Obudu, Jos, Mambilla Plateau.
5. The Ecology of Populations:
(a) Population density and overcrowding.
(b) Factors affecting population sizes:
i. Biotic (e.g. food, pest, disease, predation, competition, reproductive ability).
ii. Abiotic (e.g. temperature, space, light, rainfall, topography, pressure, pH,
etc.
(c). Ecological succession
i. primary succession
ii. secondary succession
6. Soil:
(a) Characteristics of different types of soil (sandy, loamy, clayey)
(i) Soil structure
(ii) Porosity, capillarity and humus content
(iii) Components of the soil
(i) inorganic
(ii) organic
(iii) soil organisms
(b) Soil fertility:
(i) loss of soil fertility
(ii) Renewal and maintenance of soil fertility
7. Humans and Environment:
(a) Diseases:
i Common and endemic diseases.
ii. Easily transmissible diseases and disease
syndrome such as:
– poliomyelitis
– cholera
– tuberculosis
– sexually transmitted disease/syndrome (gonorrhea, syphilis, AIDS, etc.
(b). Pollution and its control
(i) sources, types, effects and methods of control.
(ii) Sanitation and sewage
(c) Conservation of Natural Resources
(d) Game reserves and National parks
Part D: Heredity and Variations:
1. Variation in Population:
(a). Morphological variations in the physical appearance of individuals.
(i) size (height, weight)
(ii) Colour (skin, eye, hair, coat of animals, scales and feathers.
(iii) Fingerprints
(b). Physiological variation
(i) Ability to roll tongue
(ii) Ability to taste phenylthiocarbamide (PTC)
(iii) Blood groups
(c) Application of discontinuous variation in crime detection, blood transfusion and determination of paternity.
2. Heredity:
(a) Inheritance of characters in organisms;
i) Heritable and non-heritable characters.
(b) Chromosomes – the basis of heredity;
(i) Structure
(ii) Process of transmission of hereditary characters from parents to offspring.
(c) Probability in genetics and sex determination.
(d) Application of the principles of heredity in:
i) Agriculture
(ii) Medicine
(e). Sex – linked characters e.g. baldness, haemophilia, colour blindness, etc.
Part E: Evolution:
1. Theories of Evolution:
(a) Lamarck’s theory
(b) Darwin’s theory
(c) organic theory
JAMB Biology Syllabus 2026 Recommended Textbook
- Ndu, F.O. C. Ndu, Abun A. and Aina J.O. (2001) Senior Secondary School Biology: Books 1 -3, Lagos: Longman Odunfa, S.A. (2001) Essential of Biology, Ibadan: Heinemann Ogunniyi M.B. Adebisi A.A. and Okojie J.A. (2000) Biology for Senior Secondary Schools: Books 1 – 3, Macmillan Ramalingam, S.T. (2005) Modern Biology, SS Science Series. New Edition, AFP Stan. (2004) Biology for Senior Secondary Schools. Revised Edition, Ibadan: Heinemann Stone R.H. and Cozens, A.B.C. (1982) Biology for West African Schools. Longman
- Usua, E.J. (1997) Handbook of practical Biology 2nd Edition, University Press, Limited